Hierarchical models enable you to design internetworks that use specialization of function combined with a hierarchical organization. Such a design simplifies the tasks required to build a network that meets current requirements and that can grow to meet future requirements. Hierarchical models use layers to simplify the tasks for internetworking. Each layer can focus on …
Category: Cisco 300-420 Exams
Apr 20
Hierarchical Network Design – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
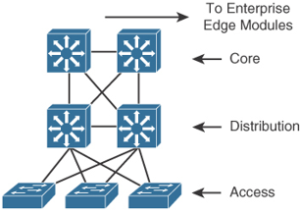
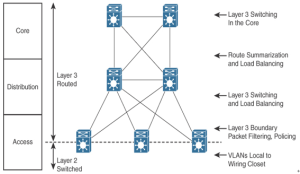
As shown in Figure 6-1, a traditional hierarchical LAN design has three layers: Figure 6-1 Hierarchical Network Design Has Three Layers: Core, Distribution, and Access Each layer provides necessary functionality to the enterprise campus network. You do not need to implement the layers as distinct physical entities. You can implement each layer in one or …
Feb 10
Access Layer – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
The access layer provides user access to local segments on the network. The access layer is characterized by switched LAN segments in a campus environment. Microsegmentation using LAN switches provides high bandwidth to workgroups by reducing the number of devices on Ethernet segments. Functions of the access layer include the following: Table 6-2 summarizes the …
Dec 12
Hub-and-Spoke Design – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
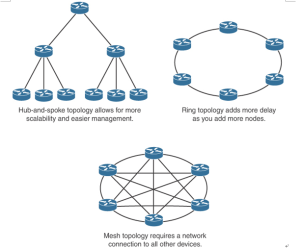
The hub-and-spoke network design (see Figure 6-5) provides better convergence times than ring topology. The hub-and-spoke design also scales better and is easier to manage than ring or mesh topologies. For example, implementing security policies in a full-mesh topology would become unmanageable because you would have to configure policies at each point location. Using the …
Sep 05
LAN Media – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
This section identifies some of the constraints you should consider when provisioning various LAN media types. It covers the physical specifications of Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit Ethernet. Ethernet Design Rules Ethernet is the underlying basis for the technologies most widely used in LANs. In the 1980s and early 1990s, most networks used 10 Mbps …
Jun 10
Gigabit Ethernet Design Rules – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
Gigabit Ethernet was first specified by two standards: IEEE 802.3z-1998 and 802.3ab-1999. The IEEE 802.3z standard specifies the operation of Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and coaxial cable and introduced the Gigabit Media-Independent Interface (GMII). These standards have been superseded by the latest revision of all the 802.3 standards included in IEEE 802.3-2002. The IEEE 802.3ab …
Apr 25
10 Gigabit Ethernet Design Rules – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
The IEEE 802.3ae supplement to the 802.3 standard, published in August 2002, specifies the standard for 10 Gigabit Ethernet. It is defined for full-duplex operation over optical media, UTP, and copper. The IEEE 802.3an standard provides the specifications for running 10 Gigabit Ethernet over UTP cabling. Hubs or repeaters cannot be used because they operate …
Feb 20
EtherChannel – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
The Cisco EtherChannel implementations provide a method to increase the bandwidth between two systems by bundling Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet links. When bundling Fast Ethernet links, use Fast EtherChannel. Gigabit EtherChannel bundles Gigabit Ethernet links. EtherChannel port bundles enable you to group multiple ports into a single logical transmission path between …
Nov 20
Comparison of Campus Media – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
As noted previously, several media types are used for campus networks. It is common to run UTP to end stations, use multiple multimode uplinks from access to distribution, and use single-mode fiber for longer-distance and higher-bandwidth links. Table 6-7 provides a summary comparison of these media. Table 6-7 Campus Transmission Media Comparison Factor Copper/UTP Multimode …
Aug 20
Spanning Tree Protocol and Layer 2 Security Design Considerations – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
Spanning Tree Protocol is defined by IEEE 802.1D. It prevents loops from being formed when switches or bridges are interconnected via multiple paths. Spanning Tree Protocol is implemented by switches exchanging BPDU messages with other switches to detect loops, which are removed by shutting down selected bridge interfaces. This algorithm guarantees that there is one …