Rapid PVST+ is based on the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) IEEE 802.1W standard. RSTP (IEEE 802.1w) natively includes most of the Cisco-proprietary enhancements to 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol, such as BackboneFast and UplinkFast. Rapid PVST+ has these unique features: Rapid PVST+ has the following roles, states, and types: Rapid PVST+ uses RSTP to provide …
Category: Cisco 300-420 Exams
Apr 20
PortFast – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
PortFast causes a Layer 2 LAN access port to enter the forwarding state immediately, bypassing the listening and learning states. When configured for PortFast, a port is still running Spanning Tree Protocol and can immediately transition to the blocking state, if necessary. PortFast should be used only when connecting a single end station to the …
Feb 20
BPDU Filter – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
BPDU Filter prevents a port from sending or receiving BPDUs. It can be configured on a per-port basis. When configured globally, it applies to all operational PortFast ports. Explicitly configuring PortFast BPDU filtering on a port that is not connected to a host can result in bridging loops. If a port configuration is not set …
Nov 20
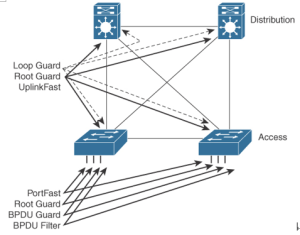
Layer 2 Security – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
Cisco provides several Layer 2 security technologies to secure the network infrastructure against various types of attacks. These include Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) security, port security, and VLAN Access Control List (VACL) security. In summary, Cisco provides several Layer 2 security technologies, such as STP security, port security, and VACL security, which can be used …
Sep 20
Campus LAN Design and Best Practices – Advanced Enterprise Campus Design
LANs can be classified as large-building LANs, campus LANs, or small and remote LANs. A large-building LAN typically contains a major data center with high-speed access and floor communications closets; it is usually the headquarters in a larger company. Campus LANs provide connectivity between buildings on a campus. Redundancy is usually a requirement in large-building …
Jul 20
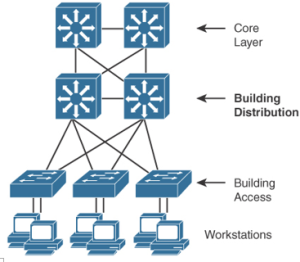
Best Practices for Hierarchical Layers – Advanced Enterprise Campus Design
Each layer of the hierarchical architecture requires special considerations. The following sections describe best practices for each of the three layers of the hierarchical architecture: access, distribution, and core. Access Layer Best Practices When designing the building access layer, you must consider the number of users or ports required to size up the LAN switch. …
May 15
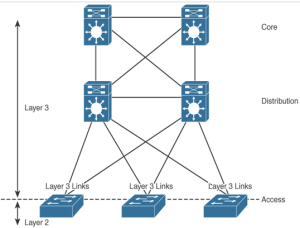
Hybrid Access Layer – Advanced Enterprise Campus Design
The hybrid access layer combines the use of Layer 2 switching with Layer 3 at the access layer. In this design, some VLANs are defined in the access layer and others in the distribution layer. There are Layer 3 and Layer 2 links between the distribution switches and the access switches. With the Layer 2 …
Mar 11
Stacking Access Switches – Advanced Enterprise Campus Design
Stacking is a method of joining multiple physical access switches into a single logical switch. Switches are interconnected by stackwise interconnect cables, and a master switch is selected. The switch stack is managed as a single object and uses a single IP management address and a single configuration file. This reduces management overhead. Furthermore, the …
Jan 15
Campus Layer Best Practices – Advanced Enterprise Campus Design
Table 7-5 summarizes campus layer best practices. Table 7-5 Campus Layer Design Best Practices Layer Best Practices Access layer Limit VLANs to a single closet, when possible, to provide the most deterministic and highly available topology. Use RPVST+ if Spanning Tree Protocol is required. It provides the best convergence. Set trunks to ON and ON …