PIM Source-Specific Multicast (PIM-SSM) is a variant of PIM-SM that builds trees that are rooted in just one source. SSM, defined in RFC 3569, eliminates the RPs and shared trees of sparse mode and only builds an SPT. SSM trees are built directly based on the receipt of group membership reports that request a given …
Category: Hierarchical Network Models
Jul 20
SNMP – IP Multicast and Network Management
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an IP application layer protocol that has become the standard for the exchange of management information between network devices. SNMP, which was initially described in RFC 1157, is a simple solution that requires little code to implement and allows vendors to build SNMP agents on their products. SNMP runs …
Mar 15
NetFlow 2 – IP Multicast and Network Management
The NetFlow export or transport mechanism sends the NetFlow data to a collection engine or network management collector. Flow collector engines perform data collection and filtering. They aggregate data from several devices and store the information. Different NetFlow data analyzers can be used, depending on the intended purpose. NetFlow data can be analyzed for the …
Jun 05
Hierarchical Network Models – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
Hierarchical models enable you to design internetworks that use specialization of function combined with a hierarchical organization. Such a design simplifies the tasks required to build a network that meets current requirements and that can grow to meet future requirements. Hierarchical models use layers to simplify the tasks for internetworking. Each layer can focus on …
Apr 20
Hierarchical Network Design – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
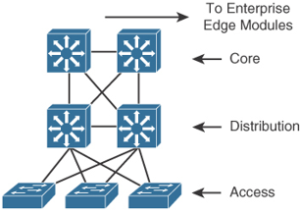
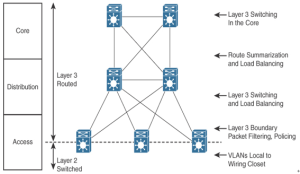
As shown in Figure 6-1, a traditional hierarchical LAN design has three layers: Figure 6-1 Hierarchical Network Design Has Three Layers: Core, Distribution, and Access Each layer provides necessary functionality to the enterprise campus network. You do not need to implement the layers as distinct physical entities. You can implement each layer in one or …
Feb 10
Access Layer – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
The access layer provides user access to local segments on the network. The access layer is characterized by switched LAN segments in a campus environment. Microsegmentation using LAN switches provides high bandwidth to workgroups by reducing the number of devices on Ethernet segments. Functions of the access layer include the following: Table 6-2 summarizes the …
Apr 25
10 Gigabit Ethernet Design Rules – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
The IEEE 802.3ae supplement to the 802.3 standard, published in August 2002, specifies the standard for 10 Gigabit Ethernet. It is defined for full-duplex operation over optical media, UTP, and copper. The IEEE 802.3an standard provides the specifications for running 10 Gigabit Ethernet over UTP cabling. Hubs or repeaters cannot be used because they operate …
Feb 20
EtherChannel – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
The Cisco EtherChannel implementations provide a method to increase the bandwidth between two systems by bundling Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet links. When bundling Fast Ethernet links, use Fast EtherChannel. Gigabit EtherChannel bundles Gigabit Ethernet links. EtherChannel port bundles enable you to group multiple ports into a single logical transmission path between …
Nov 20
Comparison of Campus Media – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
As noted previously, several media types are used for campus networks. It is common to run UTP to end stations, use multiple multimode uplinks from access to distribution, and use single-mode fiber for longer-distance and higher-bandwidth links. Table 6-7 provides a summary comparison of these media. Table 6-7 Campus Transmission Media Comparison Factor Copper/UTP Multimode …
Aug 20
Spanning Tree Protocol and Layer 2 Security Design Considerations – Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies
Spanning Tree Protocol is defined by IEEE 802.1D. It prevents loops from being formed when switches or bridges are interconnected via multiple paths. Spanning Tree Protocol is implemented by switches exchanging BPDU messages with other switches to detect loops, which are removed by shutting down selected bridge interfaces. This algorithm guarantees that there is one …
- 1
- 2