This section covers technologies used to gather network information, such as RMON, NetFlow, CDP, LLDP, and syslog.
RMON
Remote Monitoring (RMON) is a standard monitoring specification that enables network monitoring devices and console systems to exchange network monitoring data. RMON provides more information than SNMP, but it also requires more sophisticated data collection devices (network probes). RMON looks at MAC-layer data and provides aggregate information on the statistics and LAN traffic.
Enterprise networks deploy network probes on several network segments; these probes report back to the RMON console. RMON allows network statistics to be collected even if a failure occurs between a probe and the RMON console. RMON1 is defined in RFCs 1757 and 2819, and additions for RMON2 are defined in RFC 2021.
The RMON MIB is located at iso.org.dod.internet.mgt.mib.rmon or the equivalent object descriptor 1.3.6.1.2.1.16. RMON1 defines nine monitoring groups, each of which provides specific sets of data. An additional group beyond these nine is defined for Token Ring. Each group is optional, so vendors do not need to support all the groups in the MIB. Table 5-8 shows the RMON1 groups.
Table 5-8 RMON1 Groups
| Group ID | Group Name | Description |
| 1 | Statistics | Contains real-time statistics for interfaces, including packets sent, bytes, cyclic redundancy check (CRC) errors, and fragments. |
| 2 | History | Stores periodic statistical samples for later retrieval. |
| 3 | Alarm | Generates an alarm event if a statistical sample crosses a threshold. |
| 4 | Host | Provides host-specific statistics. |
| 5 | HostTopN | Lists the most active hosts. |
| 6 | Matrix | Stores statistics for conversations between two hosts. |
| 7 | Filters | Allows packets to be filtered. |
| 8 | Packet Capture | Allows packets to be captured for subsequent analysis. |
| 9 | Events | Generates event notifications. |
RMON2
RMON1 is focused on the data link and physical layers of the OSI model. As shown in Figure 5-6, RMON2 provides an extension for monitoring upper-layer protocols.
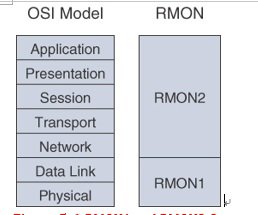
Figure 5-6 RMON1 and RMON2 Compared to the OSI Model
RMON2, defined in RFC 2021, extends the RMON group with the MIB groups listed in Table 5-9.
Table 5-9 RMON2 Groups
| Group ID | Group Name | Description |
| 11 | Protocol Directory | Lists the protocols the device supports. |
| 12 | Protocol Distribution | Provides traffic statistics for each protocol. |
| 13 | Address Mapping | Contains network-to-MAC-layer address mapping (IP address to MAC address). |
| 14 | Network Layer Host | Contains statistics for traffic sent to or from network layer hosts. |
| 15 | Network Layer Matrix | Contains statistics for conversations between two network layer hosts. |
| 16 | Application Layer Host | Contains application layer statistics for traffic sent to or from hosts. |
| 17 | Application Layer Matrix | Contains application layer statistics for conversations between pairs of hosts. |
| 18 | User History | Contains periodic samples of specified variables. |
| 19 | Probe Configuration | Probes parameter configuration. |
